Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Stay updated with the latest tips and strategies. Get additional discounts and alerts on offers.
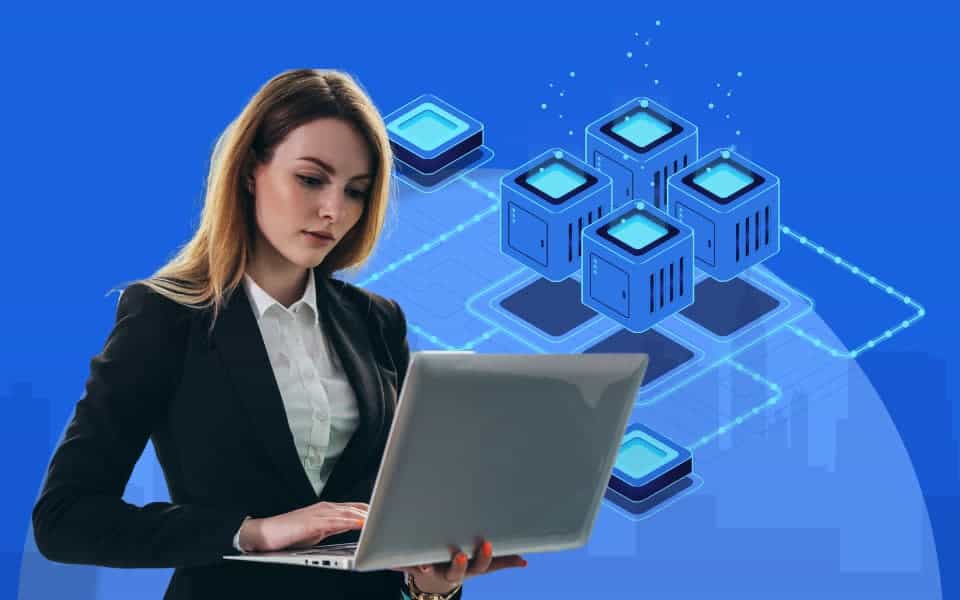


Centralized Data Storage
Data Organization

Data Security

Simplified Data Analysis

Historical Analysis

Scalability
Decision-Making

Empowering Business Intelligence
















Purpose

Structure

Scope

Integration

Performance

Usage
Data warehouse and marketing are a fusion of data-driven insights and strategic marketing efforts that has the potential to revolutionize any business. In this hyper-connected world of global markets, marketers often face the challenge of navigating through huge amounts of consumer data to deliver personalized customer experiences and drive revenue-generating conversations.










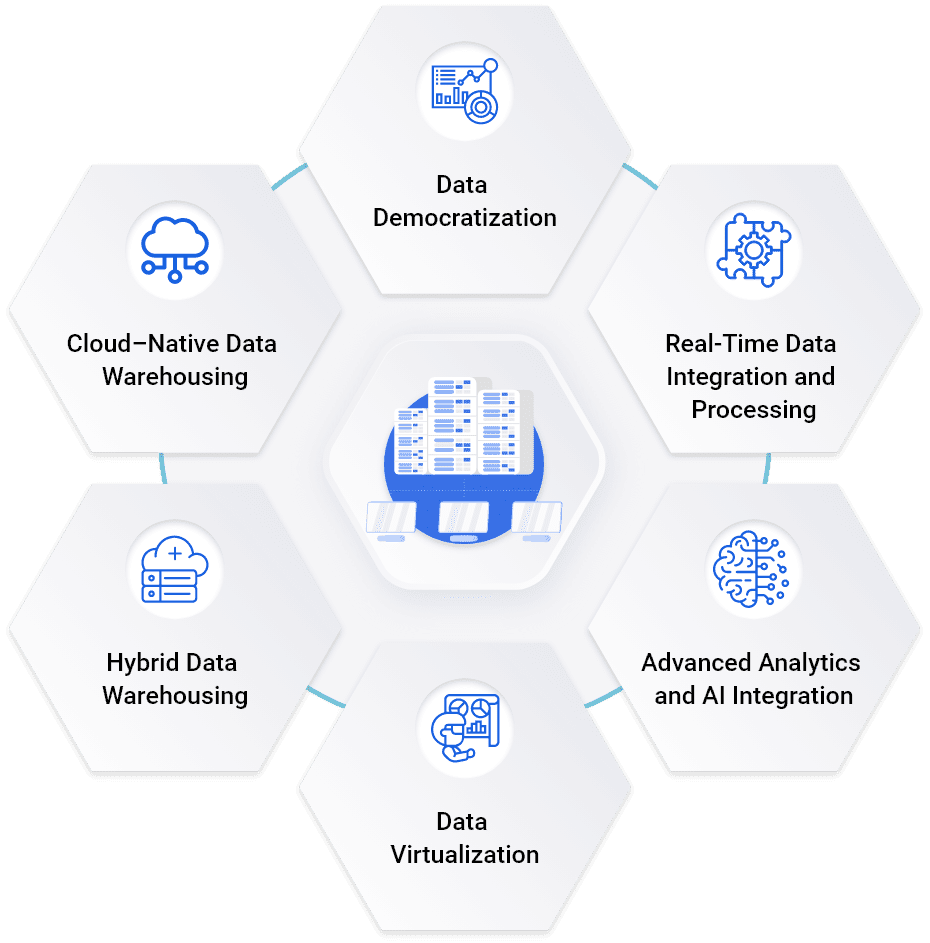






In the ever-evolving world of technology, data warehousing will remain vital to marketers. The process of transforming marketing initiatives into data-driven strategies allows businesses to unlock the full potential of their data.
Show Some Love!

Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Stay updated with the latest tips and strategies. Get additional discounts and alerts on offers.
Related Articles
Subscribe to Newsletter
Stay up to date with the latest marketing, sales, and service tips and news.
Limited Time! Celebrate the spirit of freedom with 30% OFF on all B2B databases.
Unlock high-quality leads and drive your campaigns further with accurate, verified data trusted by thousands of businesses.
Don’t miss out—power up your marketing while the offer lasts!
